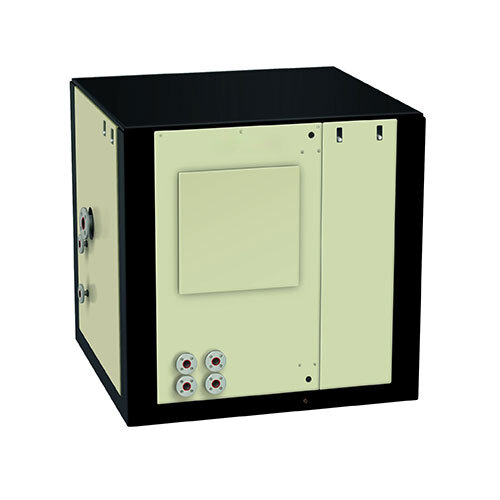
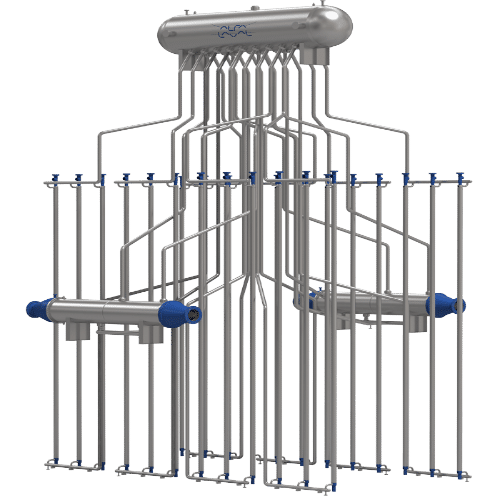
Heat Recovery from Quenching Oil
Product Details:
- Type Industrial
- Click to View more
Heat Recovery from Quenching Oil Price And Quantity
- 1 Number
Heat Recovery from Quenching Oil Product Specifications
- Industrial
Heat Recovery from Quenching Oil Trade Information
- 10 Number Per Year
- 15-20 Days
Product Description
In quenching oil systems, a Heat Recovery Unit (HRU) is employed to recover and repurpose the heat generated during the quenching process, where hot metal parts are rapidly cooled in oil to alter their mechanical properties. This process generates substantial heat, often leading to high temperatures in the oil, which can be harnessed rather than wasted.
The HRU typically works by capturing the heat from the quenching oil through a heat exchanger, transferring this thermal energy to another medium, such as water or air. This recovered heat can be used for various applications, including pre-heating oil before it enters the quenching process, heating fluids for other industrial applications, or even space heating within the facility.
Implementing a heat recovery system in quenching oil operations helps reduce the demand for external energy, lowering fuel or electricity costs and improving overall energy efficiency. Additionally, it helps to maintain optimal oil temperatures, preventing overheating and extending the life of the oil. The environmental benefits are also notable, as the reduced energy consumption lowers greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to more sustainable industrial operations. By utilizing an HRU in quenching oil systems, businesses can achieve significant savings in both energy and operational costs while promoting environmentally friendly practices.
FAQs on Heat Recovery from Quenching Oil
1. What is heat recovery from quenching oil?
Heat recovery from quenching oil involves capturing the waste heat generated during the quenching process, where hot metal parts are cooled in oil, and reusing this heat for other processes or energy needs within the facility.
2. How does heat recovery from quenching oil work?
Heat exchangers are used to transfer the heat from the hot quenching oil to another medium, like water or air, allowing the recovered heat to be reused for heating, preheating, or power generation.
3. What are the benefits of heat recovery from quenching oil?
- Energy Efficiency: Reduces the need for additional energy by utilizing recovered heat.
- Cost Savings: Lowers energy costs by making use of waste heat.
- Extended Equipment Life: Helps cool the quenching oil more effectively, extending the lifespan of equipment.
- Sustainability: Reduces energy consumption and lowers carbon emissions.
4. What types of heat exchangers are used for quenching oil heat recovery?
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers: Commonly used for high-temperature oil recovery.
- Plate Heat Exchangers: Offer efficient heat transfer in a compact design.
- Air-to-Oil Heat Exchangers: Transfer heat from quenching oil to air, which can be used in other processes.
5. What industries benefit from heat recovery from quenching oil?
Industries such as:
- Metal Processing: Recover heat during the quenching of steel or aluminum.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Reuse heat from quenching processes in parts production.
- Machinery and Equipment Manufacturing: Capture heat from the hardening process of metal components.
6. What factors should be considered when designing a quenching oil heat recovery system?
- Oil Temperature: The higher the oil temperature, the more heat can be recovered.
- Oil Composition: Ensure that the heat exchanger materials are compatible with the oil used.
- Process Requirements: The system should be designed to meet the specific heat recovery needs of the operation.
- Space and Layout: Consider the space available for installing the heat recovery equipment.
7. How much heat can be recovered from quenching oil?
The amount of heat that can be recovered depends on the temperature of the oil and the efficiency of the heat exchanger. Typically, significant amounts of energy can be captured and reused, depending on the scale of the operation.
8. How does heat recovery from quenching oil contribute to sustainability?
By reducing the need for external energy sources and repurposing waste heat, heat recovery systems help lower overall energy consumption, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and contribute to a more sustainable industrial process.
9. What maintenance is required for a quenching oil heat recovery system?
- Regular Inspection: Check for fouling, scaling, or oil buildup in the heat exchanger.
- Cleaning: Clean the heat exchanger regularly to maintain efficiency.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitor the system to ensure it is recovering heat as expected.
10. Can heat recovery systems be retrofitted into existing quenching processes?
Yes, heat recovery systems can be integrated into existing quenching oil processes with minimal disruption, helping to enhance the efficiency of the system without significant modifications.










 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free